Precise particle analysis is revolutionizing powder production by dramatically cutting waste while boosting efficiency, sustainability, and end-product consistency
Powder substances serve as essential building blocks in industries including pharmaceuticals, food manufacturing, ceramics, and personal care products
production frequently yields excessive waste because of uncontrolled variations in particle dimensions, geometry, and homogeneity
Traditional methods of powder production rely on broad assumptions and generalized controls, leading to oversized or undersized particles that must be discarded
By integrating precise particle analysis into the manufacturing workflow, companies can identify deviations in real time, adjust processing parameters dynamically, and dramatically reduce material loss
High-fidelity particle characterization is achieved through cutting-edge equipment including laser-based sizing, light scattering systems, high-res imaging, and electron microscopy techniques
They generate granular insights into size distribution curves, surface roughness, particle geometry, and tendency to form aggregates
When this data is fed into automated process control systems, manufacturers can fine-tune milling, drying, and blending operations to ensure every particle meets the required specifications
This precise oversight removes the necessity to manufacture excess material as a safety margin—a common but inefficient tradition
This methodology significantly diminishes the volume of product that must be reworked or thrown away
In the pharmaceutical industry, deviations in particle morphology can compromise tablet integrity or cause uneven drug loading, leading to costly batch rejections
With precise analysis, 動的画像解析 manufacturers can detect deviations during early stages and correct them before large volumes of material are compromised
Similarly, in the production of metal or ceramic powders used in additive manufacturing, particles that fall outside strict tolerances can cause defects in printed components
Instant feedback enables automatic segregation or recycling of non-conforming particles before they contaminate the main stream
Precise characterization also enables smarter utilization of feedstock
Knowing precisely the optimal input volume allows producers to limit overfeeding and suppress the generation of waste dust and ultrafine particles
The result is lower material expenditure, diminished waste output, and a smaller environmental footprint
Grinding and separation systems can now operate at optimal energy levels, eliminating the need to overcompensate for outdated or inaccurate monitoring
Another advantage lies in regulatory compliance and quality assurance
Pharmaceutical, food safety, and aerospace industries rely on the transparent, traceable data streams delivered by advanced particle analytics
This enhances audit readiness and ensures that every batch meets consistent standards without relying on post-production sampling, which often misses subtle inconsistencies
Demonstrating consistent quality via verifiable data fosters confidence among both consumers and oversight bodies
Implementing this technology requires investment in both equipment and personnel training
However, the return on investment is substantial
Waste reduction directly cuts landfill fees, energy demands, and overall environmental impact
Companies that adopt precise particle analysis also gain a competitive edge by improving product consistency, accelerating time to market, and enhancing brand reputation for quality and sustainability
The era of tolerating waste in powder manufacturing has ended; it is now a core operational principle
Accurate particle characterization transforms uncertainty into exactness, discard into efficiency, and inconsistency into dependable performance
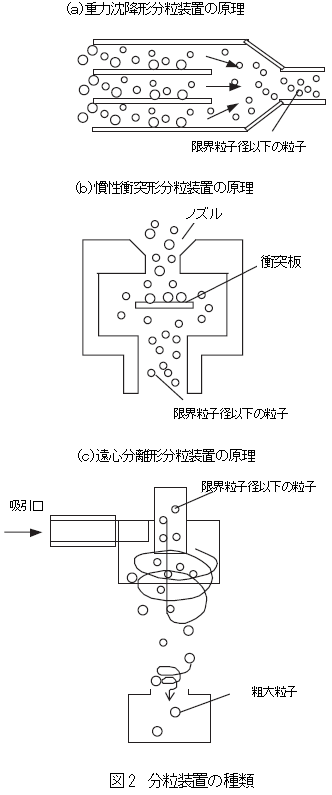
Future innovations in AI-driven analytics and automated process control will amplify the impact of particle precision
making waste reduction not just an environmental imperative but a core component of modern manufacturing excellence